Redis Modules
Redis Modules is a feature introduced in Redis 4.0 that allows developers to extend Redis functionality. Through modules, developers can define new commands, data types, and even change Redis behavior. Redis Modules greatly enhance Redis's flexibility and extensibility.
Since Redis Modules can define new data types and commands, RedisShake needs to handle these new data types and commands specifically to correctly migrate or synchronize data. Otherwise, if RedisShake doesn't understand these new data types and commands, it may fail to process the data correctly or encounter errors. Therefore, for Redis instances using Redis Modules, RedisShake generally needs corresponding adapters for the modules used to properly handle these custom data types and commands.
Supported Redis Modules
- TairHash: Hash data structure with field-level expiration and versioning support.
- TairString: String structure with versioning, enabling distributed locks and optimistic locking.
- TairZset: Supports up to 256-dimensional double sorting for multi-dimensional leaderboards.
Version Feature Support
For detailed feature support across Redis and Valkey versions, see Version Compatibility.
Unsupported Redis Modules
The following modules are currently not supported:
Redis 8 Built-in Modules:
- Vector Sets: Vector data type introduced in Redis 8 for vector similarity search
Redis Stack Modules:
- RedisJSON: JSON data type
- RediSearch: Full-text search and secondary indexing
- RedisTimeSeries: Time series database
- RedisBloom: Probabilistic data structures (Bloom filter, Cuckoo filter, Count-Min Sketch, Top-K)
- RedisGraph: Graph database (deprecated)
To migrate data using these modules, refer to How to Support New Redis Modules for adaptation, or use alternative migration solutions.
How to Support New Redis Modules
Core Process
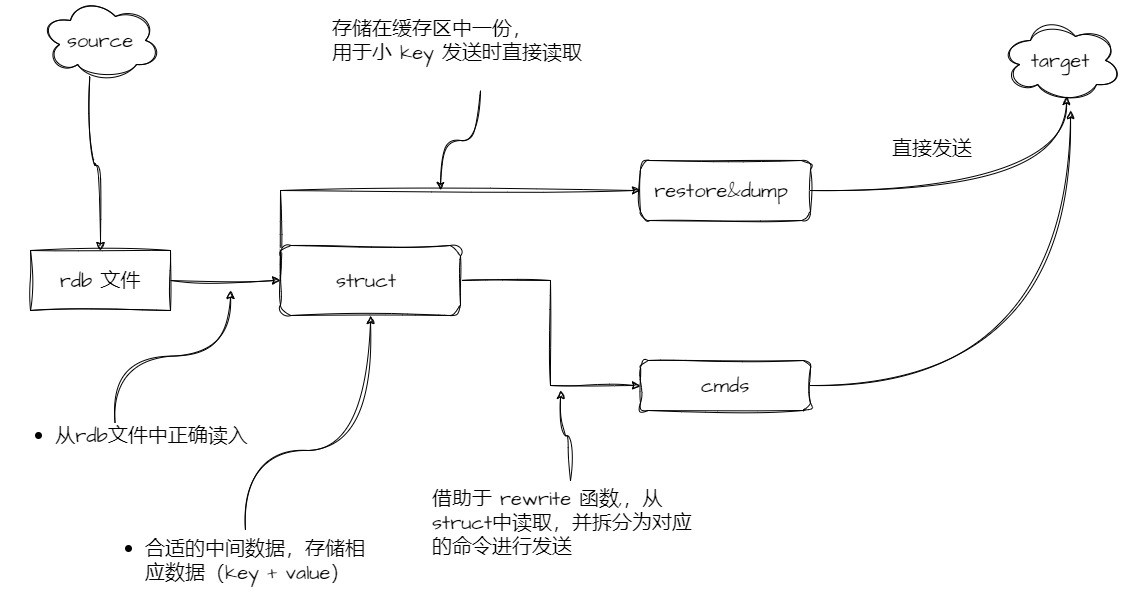
Related code is in the internal/rdb directory. To support other Redis Modules types, follow these three steps:
- Read correctly from RDB file
- RedisShake has encapsulated several types for Redis modules. When reading from RDB files, you can directly use the encapsulated functions (
internal/rdb/structure/module2_struct.go)
- RedisShake has encapsulated several types for Redis modules. When reading from RDB files, you can directly use the encapsulated functions (
- Build an appropriate intermediate data structure type to store the corresponding data (key + value)
- Handle small and large keys
- Small keys
- When executing the
LoadFromBufferfunction to read data from RDB, the corresponding value flows to two places: one is stored directly in the buffer for small key sending (related to therestorecommand), and one flows to the intermediate data structure mentioned above, used by therewritefunction described below
- When executing the
- Large keys
- Using the
rewritefunction, read from the intermediate data structure and split into corresponding commands for sending
- Using the
- Small keys
Add Command Tests
To ensure proper functionality, add the corresponding module commands in tests/helpers/commands to test that the commands work correctly in rdb, sync, and scan modes. See pybbt for the testing framework. The approach involves encapsulating the redis-py package to simulate client command sending, then comparing actual return values with expected values.
Add Command List
When transmitting large keys, RedisShake checks the command table RedisShake/internal/commands/table.go to verify command compliance. When adding a new module, you need to add the corresponding commands to the table. Refer to the code in RedisShake/scripts for examples.
Add CI
In CI testing, you need to add compilation for custom modules. See the ci.yml content for details.